Boost Employee Productivity with Rotational Shifts: The ultimate Guide

Did you know that rotational shifts can increase employee productivity by 20%? In today’s fast-paced business world, many companies are adopting rotational shift schedules to meet the growing demand for 24/7 operations. But what exactly are rotational shifts, and how can organizations implement them effectively?
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits, challenges, and best practices of rotational shifts, providing insights and strategies for HR professionals and business leaders.
What Are Rotational Shifts?
Rotational shifts, also known as Rotating Shifts, are work schedules where employees alternate between different shift times (e.g., morning, afternoon, night) on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis. This system ensures that all employees share the responsibility of working less desirable hours, such as overnight or weekend shifts.
Rotational shifts are common in industries that require continuous coverage, such as healthcare, manufacturing, hospitality, and transportation. By implementing a rotational schedule, businesses can provide better customer service, ensure uninterrupted operations, and optimize their workforce.
Benefits of Rotational Shifts
- Increased Flexibility
Rotational shifts offer flexibility for both employers and employees. Businesses can align their workforce availability with production demands, avoiding overstaffing during quiet periods and understaffing at peak times. Employees can organize their personal lives and plan their commitments accordingly, leading to improved work-life balance.
- Skill Diversification
By working in different roles or departments, employees can develop diverse skills and become more versatile. This cross-training not only benefits the individual but also strengthens the overall team dynamic, making the workforce more adaptable and well-rounded.
- Employee Satisfaction
Rotational shifts can help prevent burnout and increase job satisfaction. By sharing the burden and benefits of different shifts, the system promotes fairness among staff, improving workplace morale. Additionally, the variety of tasks keeps employees engaged and motivated.
Challenges of Rotational Shifts
- Work-Life Balance
Inconsistent scheduling can disrupt employees’ personal lives and routines. Changing shifts can make it difficult for employees to coordinate their schedules with family commitments, social activities, and personal routines.
- Scheduling Complexities
Managing rotational shifts requires careful planning and coordination. Employers must ensure that the right number of skilled employees are available for each shift while considering factors such as leave requests, training needs, and employee preferences.
- Health and Well-being
Rotating shifts can mess with employees’ sleep, causing tiredness and fatigue. Over time, irregular work hours can lead to serious health issues, including heart problems, stomach issues, and mental health concerns.
Best Practices for Implementing Rotational Shifts
- Clear Communication
Effective communication is key to the successful implementation of rotational shifts. Employers should clearly communicate shift schedules, expectations, and any changes to employees well in advance. Regular feedback sessions can help address concerns and improve the overall process.
- Support Systems
To reduce the negative impacts of rotational shifts, employers should provide support systems for employees. This may include counseling services, flexible scheduling options, and resources for managing sleep and health issues. By prioritizing employee well-being, organizations can foster a positive work environment and reduce turnover.
- Continuous Improvement
Rotational shift schedules should be regularly reviewed and adjusted based on employee feedback, business needs, and industry best practices. By continuously improving the system, employers can optimize productivity, enhance employee satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Conclusion
Rotational shifts offer a range of benefits for both employers and employees, but they also come with unique challenges. By understanding the complexities of rotational shifts and implementing best practices, organizations can create a work environment that is productive, engaging, and supportive for all employees. A Gitnux Report states that 90% of workers prioritize flexible timings and work-life balance while selecting a job.
As you consider adopting rotational shifts in your organization, remember to prioritize clear communication, employee well-being, and continuous improvement. With the right strategies in place, rotational shifts can be a powerful tool for driving business success and fostering a thriving workforce.
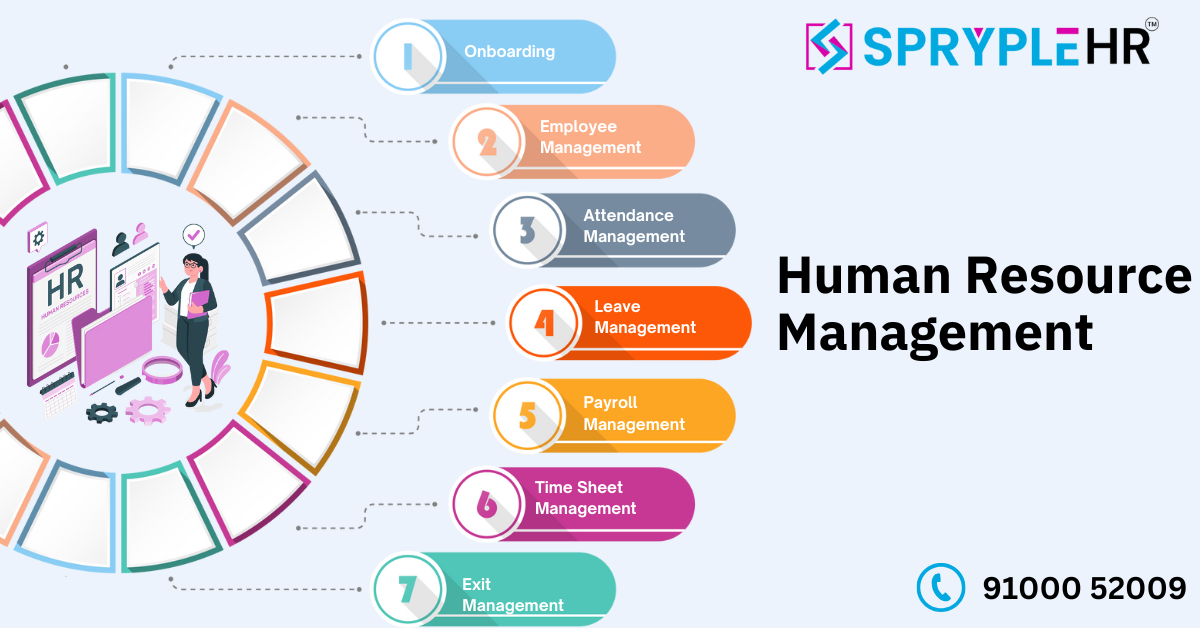
How SprypleHR Can Help
SprypleHR is an advanced, AI-enabled HR solution designed to streamline the management of rotational shifts. With features like AI-powered scheduling, real-time shift management, and comprehensive analytics, SprypleHR can help you implement and manage rotational shifts effectively, ensuring your workforce remains productive and satisfied.